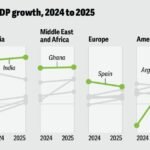
In 2025, geopolitical tensions are no longer just headline news—they’re actively reshaping how the world does business. As rivalries between global powers intensify and regional conflicts escalate, international trade is being transformed. Businesses, governments, and consumers are all feeling the impact as the rules of global commerce are rewritten.
In this article, we explore how current geopolitical conflicts and power struggles are influencing global trade and supply chains—and what it means for the future.
What Are Geopolitical Tensions?
Geopolitical tensions refer to conflicts and strategic rivalries between countries or regions. These tensions can be driven by:
- Territorial disputes
- Economic competition
- Military conflicts
- Political ideologies
- Access to natural resources
Such tensions often result in trade restrictions, sanctions, tariffs, or even complete disruption of international commerce.
How Geopolitical Conflicts Are Reshaping Trade in 2025
1. The US-China Economic Rivalry
The power struggle between the United States and China has redefined global trade patterns. The two largest economies are locked in a long-term strategic competition, affecting industries from technology to green energy.
Key Impacts:
- Export controls on semiconductors and AI technologies
- Tariffs and trade restrictions on critical goods
- Countries diversifying supply chains to avoid reliance on either side
2. Russia-Ukraine War
The war in Ukraine has triggered widespread disruptions, especially in energy and food markets. Sanctions on Russia and reduced exports from both nations have had ripple effects across Europe, Africa, and Asia.
Key Impacts:
- Spikes in oil and gas prices
- Global grain shortages and food insecurity
- Investment in alternative energy sources and agricultural supply chains
3. Middle East Tensions
Ongoing instability in the Middle East—including tensions involving Iran, Israel, and Gulf countries—continues to threaten the stability of global oil supply and maritime trade routes.
Key Impacts:
- Fluctuating fuel prices
- Disruptions in key shipping lanes like the Strait of Hormuz
- Rising logistics and insurance costs for international shipping
4. China-Taiwan Strait Dispute
The growing friction between China and Taiwan is particularly worrying for the global tech industry. Taiwan is home to some of the world’s most advanced semiconductor manufacturing.
Key Impacts:
- Risk of chip shortages for electronics and automotive industries
- Increased stockpiling of critical components
- Search for alternative tech manufacturing hubs
How Businesses Are Responding
As uncertainty grows, companies are adjusting strategies to reduce risk and increase resilience.
✅ Diversifying Supply Chains
Many businesses are moving away from China-centric supply models. Countries like Vietnam, India, Mexico, and Poland are becoming alternative hubs for manufacturing and sourcing.
✅ Nearshoring and Reshoring
Firms are relocating operations closer to home markets to minimize disruptions. This trend is growing in the US, EU, and parts of Asia.
✅ Building Strategic Alliances
Nations are signing new trade agreements with trusted partners to create secure economic zones. Examples include:
- The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
- The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)
- Strengthened EU–Latin America trade agreements
✅ Geopolitical Risk Management
Companies are investing in political intelligence, monitoring systems, and crisis response plans to stay ahead of sudden changes in trade regulations or conflict zones.
Who’s Winning and Who’s Losing?
🌍 Winners:
- India, Vietnam, and Mexico – gaining from supply chain diversification
- Energy exporters like the U.S. and Brazil – benefiting from high global demand
- Neutral trade hubs like UAE and Singapore – emerging as financial and logistics centers
🌍 Losers:
- Countries reliant on a single trade partner
- Regions caught in political conflict zones
- Businesses unprepared for political risk and regulation shifts
The Future of Global Trade: Fragmentation or Innovation?
The era of free, frictionless global trade is giving way to a new model defined by strategic competition, security concerns, and economic nationalism.
While fragmentation poses challenges, it also opens doors for innovation:
- More regional cooperation
- Technological breakthroughs in logistics and manufacturing
- Greater investment in local resilience and sustainability
Last modified: April 19, 2025