Edge Computing
Introduction
Edge computing is a buzzword that’s been floating around tech circles lately, but what exactly does it mean? More importantly, why should you care? Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or a business owner, understanding edge computing can give you a leg up in a world that’s increasingly reliant on digital solutions. In this article, we’ll dive into the nitty-gritty of edge computing, explore its benefits, and see why it’s becoming such a pivotal part of modern technology.
The Basics of Edge Computing
What is Edge Computing?
At its core, edge computing is all about bringing computation and data storage closer to where it’s needed. Instead of relying solely on centralized data centers (like in traditional cloud computing), edge computing processes data at the “edge” of the network. This means that data is handled locally, on devices or local servers, rather than being sent back and forth to a remote data center.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Imagine you’re using a smart home device, like a thermostat. Instead of your thermostat sending data to a faraway server, waiting for a response, and then acting on it, edge computing allows the device to process information locally. This results in faster response times and reduces the load on central servers. By placing computation near the source of data, edge computing minimizes latency and enhances the performance of applications.
The Evolution of Computing
From Centralized to Decentralized Computing
Computing has come a long way from the days of massive, centralized mainframes. Initially, all processing was done in one place, which worked fine when data and user requests were limited. However, as the amount of data grew, the need for more efficient processing methods became apparent.
The Rise of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing revolutionized the way we handle data by offering scalable resources over the internet. Companies no longer needed to invest heavily in their data centers; instead, they could leverage the cloud for storage and processing power. However, as useful as cloud computing is, it’s not without its drawbacks, such as latency issues and bandwidth limitations.
The Shift to Edge Computing
Enter edge computing. This paradigm shift addresses the shortcomings of cloud computing by decentralizing data processing. By performing computations closer to the data source, edge computing reduces latency and improves the efficiency of applications, especially those requiring real-time processing.
Key Components of Edge Computing
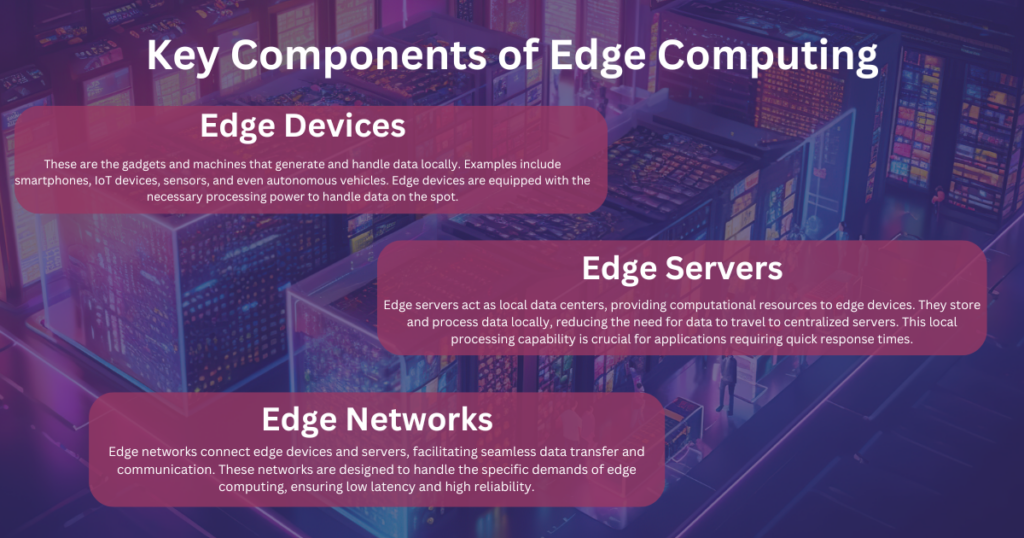
Edge Devices
These are the gadgets and machines that generate and handle data locally. Examples include smartphones, IoT devices, sensors, and even autonomous vehicles. Edge devices are equipped with the necessary processing power to handle data on the spot.
Edge Servers
Edge servers act as local data centers, providing computational resources to edge devices. They store and process data locally, reducing the need for data to travel to centralized servers. This local processing capability is crucial for applications requiring quick response times.
Edge Networks
Edge networks connect edge devices and servers, facilitating seamless data transfer and communication. These networks are designed to handle the specific demands of edge computing, ensuring low latency and high reliability.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Reduced Latency
One of the most significant advantages of edge computing is reduced latency. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing minimizes the time it takes for data to travel back and forth to a central server. This is especially important for applications like autonomous vehicles and real-time analytics.
Improved Reliability
Edge computing enhances the reliability of applications by reducing dependency on a central server. Even if there’s a network disruption, local processing ensures that critical functions can continue without interruption.
Enhanced Security
Handling data locally can also bolster security. Sensitive information doesn’t need to travel across the internet to a central server, reducing the risk of interception or breaches. Moreover, edge computing allows for localized data compliance, adhering to regional data protection regulations.
Cost Efficiency
By offloading processing tasks to edge devices and servers, companies can reduce their reliance on expensive centralized data centers. This can lead to significant cost savings, especially for businesses dealing with large volumes of data.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices are a prime example of edge computing in action. Smart sensors and devices generate vast amounts of data that need to be processed quickly and efficiently. Edge computing allows these devices to operate smoothly without overwhelming central servers.
Autonomous Vehicles
For autonomous vehicles, split-second decision-making is crucial. Edge computing enables these vehicles to process data locally, ensuring rapid response times and enhancing safety on the road.
Smart Cities
Smart city initiatives rely on real-time data from various sources like traffic cameras, weather sensors, and public transportation systems. Edge computing facilitates the immediate processing of this data, helping cities operate more efficiently and respond to issues promptly.
Healthcare
In healthcare, edge computing can improve patient outcomes by enabling real-time data processing for medical devices and telemedicine applications. This allows for faster diagnostics and more responsive care.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
Differences and Similarities
While both edge and cloud computing aim to enhance data processing, they do so in different ways. Cloud computing centralizes data in remote servers, providing scalable resources but often suffering from latency issues. In contrast, edge computing decentralizes data processing, bringing it closer to the data source to reduce latency and improve efficiency.
When to Use Edge vs. Cloud Computing
Edge computing is ideal for applications requiring real-time processing and low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, IoT, and smart cities. On the other hand, cloud computing is suitable for tasks that need vast computational power and storage, such as Big data analytics and large-scale machine learning.
Challenges in Edge Computing
Security Concerns
While edge computing can enhance security by processing data locally, it also introduces new challenges. Edge devices can be vulnerable to physical tampering, and ensuring consistent security across a decentralized network can be complex.
Infrastructure Complexity
Implementing edge computing requires a robust and reliable infrastructure. This involves setting up numerous edge devices and servers, which can be a daunting task for businesses without the necessary expertise.
Data Management
Managing data across a decentralized network presents unique challenges. Ensuring data consistency, integrity, and compliance with regulations requires sophisticated management strategies and tools.
Future of Edge Computing
Technological Advancements
As technology continues to evolve, so too will edge computing. Advances in hardware, software, and network technologies will further enhance the capabilities and efficiency of edge computing systems.
Market Trends
The edge computing market is poised for significant growth. With the increasing adoption of IoT, 5G, and artificial intelligence, the demand for edge computing solutions is expected to rise, driving innovation and investment in this field.
Potential Impacts on Various Industries
Edge computing can potentially transform numerous industries, from healthcare and automotive to manufacturing and retail. By enabling real-time data processing and decision-making, edge computing can improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and drive business growth.
Conclusion
Edge computing represents a significant shift in how we handle data and perform computations. By bringing processing power closer to the data source, edge computing reduces latency, improves reliability, enhances security, and offers cost efficiencies. As technology continues to advance, the importance of edge computing will only grow, making it a critical component of the digital landscape. Whether you’re a business looking to enhance your operations or a tech enthusiast eager to stay ahead of the curve, understanding edge computing is essential.
FAQs
What is the difference between edge computing and fog computing?
Fog computing is a subset of edge computing. While both involve processing data closer to the source, fog computing extends the concept by including a network layer that processes data between edge devices and the cloud. This helps in managing and analyzing data more efficiently.
How does edge computing enhance IoT?
Edge computing enhances IoT by allowing devices to process data locally, leading to faster response times and reduced reliance on central servers. This is crucial for real-time applications and helps in managing the massive data generated by IoT devices.
Can edge computing improve gaming experiences?
Yes, edge computing can significantly improve gaming experiences by reducing latency. By processing game data closer to the player, edge computing ensures smoother and more responsive gameplay, enhancing the overall gaming experience.
What industries benefit the most from edge computing?
Industries like healthcare, automotive, manufacturing, and smart cities benefit significantly from edge computing. These sectors rely on real-time data processing and quick decision-making, which edge computing facilitates.
Is edge computing secure?
While edge computing can enhance security by localizing data processing, it also presents new security challenges. Protecting decentralized networks and ensuring device security requires robust strategies and ongoing vigilance.









