Will Cryptocurrency Ever Replace Traditional Money?
In recent years, cryptocurrency has become a buzzword, capturing the interest of investors, technologists, and even governments. But can it ever fully replace traditional money? Let’s dive deep into this topic and explore the potential future of our financial systems.
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments and central banks, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology. Bitcoin, created in 2009 by an unknown person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, was the first cryptocurrency and remains the most well-known. Other popular cryptocurrencies include Ethereum, Ripple (XRP), and Litecoin.
Traditional Money: An Overview
Traditional money, also known as fiat money, is the currency that governments issue and regulate. It comes in physical forms like coins and banknotes and digital forms used in bank accounts and electronic transactions. The history of traditional money dates back thousands of years, evolving from bartering systems to coins, paper money, and now digital transactions facilitated by banks and financial institutions.
Key Differences Between Cryptocurrency and Traditional Money
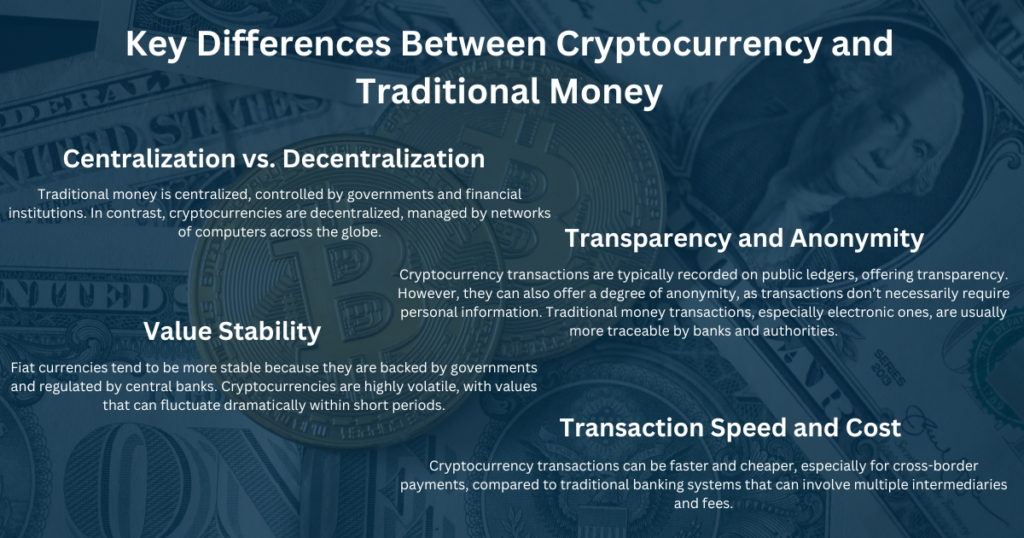
Centralization vs. Decentralization
Traditional money is centralized, controlled by governments and financial institutions. In contrast, cryptocurrencies are decentralized, managed by networks of computers across the globe.
Transparency and Anonymity
Cryptocurrency transactions are typically recorded on public ledgers, offering transparency. However, they can also offer a degree of anonymity, as transactions don’t necessarily require personal information. Traditional money transactions, especially electronic ones, are usually more traceable by banks and authorities.
Value Stability
Fiat currencies tend to be more stable because they are backed by governments and regulated by central banks. Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile, with values that can fluctuate dramatically within short periods.
Transaction Speed and Cost
Cryptocurrency transactions can be faster and cheaper, especially for cross-border payments, compared to traditional banking systems that can involve multiple intermediaries and fees.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency Over Traditional Money
Lower Transaction Fees
Cryptocurrencies often have lower transaction fees compared to traditional banking and remittance services. This can be particularly beneficial for international transactions.
Increased Security
The decentralized and cryptographic nature of cryptocurrencies can offer enhanced security, making it harder for fraud and counterfeiting to occur.
Accessibility
Cryptocurrencies can provide financial services to unbanked populations in developing regions, offering greater financial inclusion.
Speed of Transactions
Cryptocurrency transactions can be processed quickly, sometimes within minutes, regardless of the transaction amount or the parties’ locations.
Disadvantages of Cryptocurrency
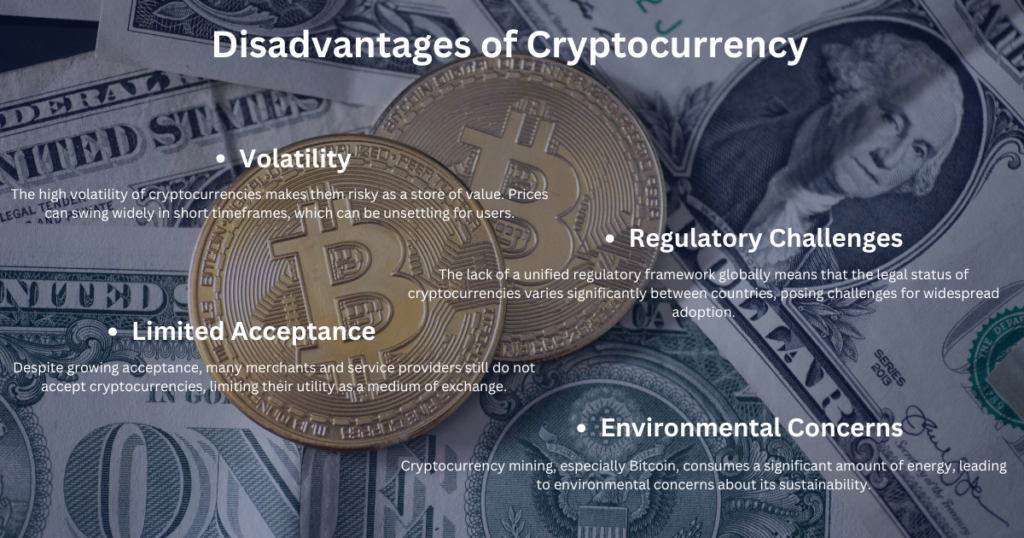
Volatility
The high volatility of cryptocurrencies makes them risky as a store of value. Prices can swing widely in short timeframes, which can be unsettling for users.
Regulatory Challenges
The lack of a unified regulatory framework globally means that the legal status of cryptocurrencies varies significantly between countries, posing challenges for widespread adoption.
Limited Acceptance
Despite growing acceptance, many merchants and service providers still do not accept cryptocurrencies, limiting their utility as a medium of exchange.
Environmental Concerns
Cryptocurrency mining, especially Bitcoin, consumes a significant amount of energy, leading to environmental concerns about its sustainability.
Adoption of Cryptocurrency: Current Trends
Businesses Accepting Cryptocurrency
More businesses are beginning to accept cryptocurrencies as payment, from small retailers to major companies like Tesla and Microsoft. This trend is slowly increasing the practical utility of cryptocurrencies.
Countries Exploring Digital Currencies
Several countries are exploring or have launched their own digital currencies. China’s digital yuan is one of the most notable examples. These government-backed digital currencies could coexist with or even compete against cryptocurrencies.
Public Perception and Use
Public interest in cryptocurrencies continues to grow, with more people investing in and using digital currencies for various transactions. However, skepticism remains due to volatility and security concerns.
Challenges to Replacing Traditional Money
Regulatory Hurdles
For cryptocurrencies to replace traditional money, significant regulatory hurdles must be overcome. Governments would need to establish clear frameworks that ensure security and stability while allowing innovation.
Technological Infrastructure
The current financial infrastructure is deeply entrenched and robust. Replacing it with a new system based on cryptocurrency would require significant technological advancements and widespread adoption.
Economic Impact
Transitioning to a cryptocurrency-based system could have profound economic impacts, including on banking systems, monetary policy, and global trade. These impacts need careful consideration.
Trust and Acceptance
For cryptocurrencies to replace traditional money, they must gain widespread trust and acceptance. This requires addressing issues like volatility, security, and ease of use.
Potential Future Scenarios
Cryptocurrency Fully Replacing Traditional Money
In a highly optimistic scenario, cryptocurrency could replace traditional money entirely. This would require overcoming all the current challenges and achieving universal acceptance and trust.
Coexistence of Cryptocurrency and Traditional Money
A more likely scenario is the coexistence of cryptocurrencies and traditional money. Cryptocurrencies could serve as an alternative or complement to fiat money, offering more options for users.
Cryptocurrency as a Niche Financial Tool
Cryptocurrencies might remain a niche financial tool used for specific purposes, such as international remittances, investments, or as a hedge against inflation.
Case Studies: Countries and Cryptocurrency
El Salvador
El Salvador made headlines by becoming the first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender in 2021. This experiment aims to boost financial inclusion and attract investment but has faced criticism and challenges.
China
China has taken a different approach by developing its own digital currency, the digital yuan. This state-controlled digital currency aims to modernize payments while maintaining government oversight.
European Union
The European Union is also exploring the potential of a digital euro, aiming to provide a secure and efficient digital payment option that complements cash and other forms of electronic payments.
Technological Innovations in Cryptocurrency
Blockchain Advancements
Innovations in blockchain technology are addressing some of the scalability and security issues that currently limit the widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies. For instance, the development of Layer 2 solutions like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Plasma for Ethereum aims to significantly increase transaction throughput and reduce fees. Moreover, advancements in consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), are making blockchain networks more energy-efficient and scalable. These technological improvements are crucial for handling larger volumes of transactions and supporting a broader range of applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to supply chain management.
Security Improvements
Ongoing improvements in cryptographic techniques and security protocols are enhancing the safety and reliability of cryptocurrency transactions. Integrating zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) and homomorphic encryption into blockchain systems ensures data privacy and integrity without losing transparency. Additionally, multi-signature wallets and hardware security modules (HSMs) add extra protection for digital assets. These advancements build trust in cryptocurrency security, making them more attractive to individual and institutional investors.
Cross-Border Payments
Cryptocurrencies are now widely utilized for cross-border payments, presenting a swifter and more cost-effective alternative to traditional international banking systems. Unlike conventional banking methods that may take several days and incur high fees due to multiple intermediaries, cryptocurrency transactions can be completed within minutes at minimal costs. This efficiency is particularly advantageous for remittances, enabling individuals to send money to family members in other countries quickly and affordably. Additionally, blockchain technology facilitates transparent transaction tracking, reducing the risk of fraud and fostering trust between parties. Consequently, cryptocurrencies are emerging as a viable option for facilitating global commerce and international trade.
Economic and Social Implications
Impact on Banks and Financial Institutions
The rise of cryptocurrencies could significantly impact banks and financial institutions, potentially reducing their role in the financial system and forcing them to adapt.
Effects on Global Trade
Cryptocurrencies could simplify and speed up global trade by providing a universal medium of exchange that transcends national borders.
Social Equity and Financial Inclusion
Cryptocurrencies have the potential to improve social equity by providing access to financial services for unbanked and underbanked populations worldwide.
Expert Opinions: Will Cryptocurrency Ever Replace Traditional Money
Perspectives from Economists
Economists are divided on the future of cryptocurrencies. Some see them as a revolutionary financial innovation, while others are skeptical about their long-term viability and stability.
Views from Technology Experts
Technology experts often emphasize the potential of blockchain and cryptocurrencies to transform various industries, beyond just finance.
Financial Industry Insights
The financial industry is cautiously exploring the integration of cryptocurrencies, balancing the opportunities for innovation with the risks of volatility and regulatory challenges.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency has undoubtedly changed the financial landscape, offering new possibilities for transactions, investments, and financial inclusion. However, the question of whether it will ever replace traditional money is complex and multifaceted. While cryptocurrencies offer significant advantages, they also face substantial challenges. The future may likely see a coexistence of cryptocurrencies and traditional money, each serving different needs and purposes.
FAQs
What are the risks of investing in cryptocurrency? Investing in cryptocurrency is risky due to its high volatility, regulatory uncertainties, and potential security vulnerabilities.
How does cryptocurrency impact the environment? Cryptocurrency mining, especially Bitcoin, consumes a significant amount of energy, leading to environmental concerns about carbon footprints and sustainability.
Can cryptocurrency be hacked? While the blockchain technology behind cryptocurrencies is secure, individual accounts and exchanges can be vulnerable to hacking and other security breaches.
What are the benefits of using cryptocurrency? Benefits include lower transaction fees, increased security, faster transactions, and greater accessibility, especially for unbanked populations.
How can I start using cryptocurrency? To start using cryptocurrency, you can set up a digital wallet, choose a reputable exchange to buy and sell cryptocurrencies, and familiarize yourself with the basic principles of how they work.








